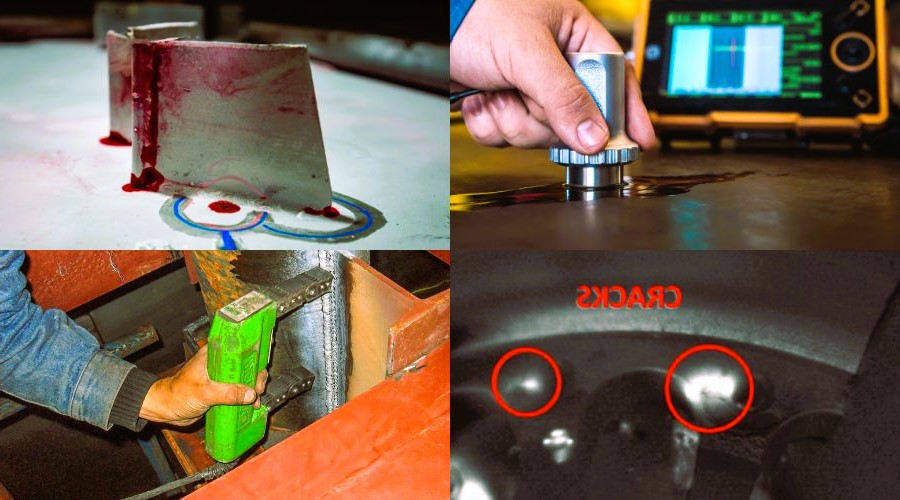
Exploring Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Methods in Production
BlogNon-Destructive Testing (NDT) is a crucial component of quality assurance in the manufacturing industry. Unlike traditional testing methods that may damage or alter the integrity of materials, NDT allows for the examination of materials and components without causing harm. In this article, we will explore various Non-Destructive Testing methods employed in production processes, shedding light on their applications and significance in ensuring product integrity.
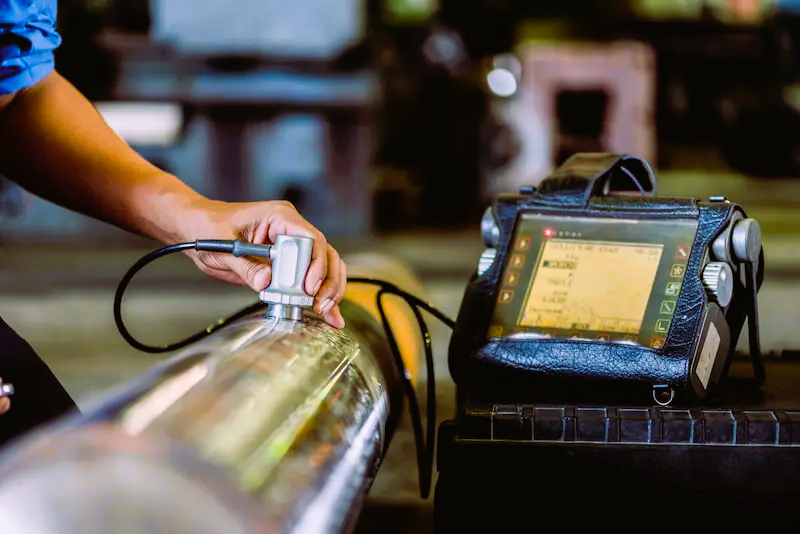
1. Ultrasonic Testing (UT):
Ultrasonic Testing is a widely used NDT method that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to inspect materials for internal flaws or defects. In production, UT is employed to assess the thickness of materials, detect voids, and identify internal discontinuities such as cracks or inclusions. This method is particularly effective for metals, composites, and other solid materials, providing detailed insights into the structural integrity of components.
2. Radiographic Testing (RT):
Radiographic Testing involves the use of X-rays or gamma rays to inspect the internal structure of materials. In production testing, RT is valuable for detecting internal defects, voids, and inconsistencies. It is commonly used in industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing to assess the integrity of welds, castings, and complex structures. RT provides detailed images that aid in identifying potential issues without compromising the structural integrity of the tested materials.

3. Eddy Current Testing (ECT):
Eddy Current Testing is a non-contact NDT method that utilizes electromagnetic induction to assess the conductivity and integrity of materials. In production, ECT is employed to detect surface cracks, measure coating thickness, and identify variations in material properties. This method is particularly useful for inspecting conductive materials such as metals and is widely applied in industries ranging from electronics to aerospace.
4. Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT):
Magnetic Particle Testing is a surface inspection method that detects surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials. In production, MPT is commonly used for assessing welds, castings, and forgings. The process involves applying magnetic particles to the surface of the material and observing their behavior under the influence of a magnetic field. MPT is efficient for detecting cracks, discontinuities, and other surface anomalies. Maximizing Efficiency: Lean Principles in Production Testing.
5. Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT):
Liquid Penetrant Testing is a versatile NDT method used to detect surface defects in non-porous materials. In production, LPT is employed to assess the integrity of components such as welds, castings, and machined parts. The process involves applying a liquid penetrant to the material’s surface, allowing it to seep into surface cracks or discontinuities. After a specified dwell time, excess penetrant is removed, and a developer is applied to reveal any penetrant trapped in defects.
6. Visual Testing (VT):
Visual Testing, although a basic method, remains a fundamental component of NDT in production. Visual inspection involves a thorough examination of materials, components, and welds using the naked eye or aided by optical instruments. In production settings, VT serves as a primary method for detecting surface irregularities, corrosion, and physical damage. It is often complemented by other NDT methods for a comprehensive assessment.
Applications and Significance in Production:
- Weld Inspection: NDT methods play a crucial role in inspecting welds for defects such as cracks, lack of fusion, and porosity. Techniques like Radiographic Testing and Ultrasonic Testing are commonly used to assess the integrity of weld joints in various industries, ensuring the structural soundness of fabricated structures.
- Material Thickness Measurement: Ultrasonic Testing is instrumental in measuring the thickness of materials, particularly in scenarios where corrosion or wear may affect structural integrity. This application is vital in industries such as oil and gas, where the condition of pipelines and vessels must be closely monitored.
- Quality Control in Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, NDT methods are extensively used to ensure the quality and safety of components such as aircraft engines, wings, and structural elements. Radiographic Testing, Eddy Current Testing, and Ultrasonic Testing are applied to detect defects that could compromise the performance of aerospace components.
- Railway Inspection: Magnetic Particle Testing is commonly employed in the railway industry to inspect the integrity of critical components such as rail tracks and welded joints. This method helps identify surface cracks and discontinuities, contributing to the overall safety and reliability of railway infrastructure.
Linking to Standards:
The application of NDT methods in production aligns with industry standards that establish guidelines for quality assurance. Standards ensure that NDT processes are executed consistently and reliably, contributing to the overall integrity of manufactured products. For more information on standards in Canada, you can refer to authoritative sources such as Wikipedia.
Conclusion: Enhancing Quality Assurance in Production
Non-Destructive Testing methods play a pivotal role in enhancing quality assurance in production processes. From weld inspections to material thickness measurements, these methods provide manufacturers with valuable insights into the structural integrity of materials and components. The significance of NDT in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and oil and gas underscores its role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and compliance of manufactured products.
As technology continues to advance, the evolution of NDT methods is expected to bring even more sophisticated and efficient techniques to the production testing landscape. Manufacturers embracing these advancements are well-positioned to uphold the highest standards of quality and safety in their products, contributing to the overall advancement of the manufacturing industry.
Recent Posts
- The Role of Data Analytics in Optimizing Production Testing Processes
- Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators for Production Testing
- The Interplay Between Production Testing and Continuous Improvement
- The Importance of Training and Skill Development in Production Testing Teams
- Strategies for Minimizing Downtime During Production Testing